Momentum Meaning in Physics
Momentum is a vector quantity. A solid undergraduate background in classical physics electromagnetic theory including Maxwells equations and mathematical familiarity with partial differential equations and complex.

Momentum Definition Momentum Symbol Is Defined As The Product Of The And Of A Moving Body Momentum P Units N B Since Ppt Download
Spin In classical physics a rotating object possesses a property known as angular momentum.

. In words it could be said that the force times the time equals the mass times the change in velocity. The magnitude of spin is quantized meaning that it can only take on a limited set of discrete values. Or abbreviating p1 p2 P total momentum this is.
The linear momentum of a particle is defined as the product of the mass of the particle times the velocity of that particle. It tells us that the total x component of the momentum is conserved and the total y component of the momentum is conserved. In physics the quantity Force time is known as impulse.
Thus an objects kinetic energy is defined mathematically by the following equation. Momentum product of the mass of a particle and its velocity. The course is intended only as a first plasma physics course but includes what I take to be the critical concepts needed for a foundation for further study.
Thomas Young 17731829 derived a similar formula in 1807 although he neglected to add the ½ to the front and he didnt use the words mass and weight with the same precision we do nowadays. Here will discuss the concept of impulse in detail and understand how it is applied to different situations. Before we fully understand what is impulse let us try to understand the concept of momentum.
And since the quantity mv is the momentum the quantity mΔv must be the change in. When the interaction ceases the two objects no longer experience the force. Forces only exist as a result of an interaction.
Naturally the kinetic energy of an object at rest should be zero. A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the objects interaction with another object. We said then merely that the total energy in the world is constant.
Ie it has both magnitude and direction. Contact versus Action-at-a-Distance Forces. See Newtons laws of motion.
If m is an objects mass and v is its velocity also a vector quantity then the objects momentum p is. Angular momentum behaves similarly. Students will also learn the relation between impulse and momentum along with suitable examples.
Very early in Volume I we discussed the conservation of energy. It is a vector quantity possessing a magnitude and a direction. In the International System of Units SI the unit of measurement of.
714 Collisions When we talk about a collision in physics between two particles say we. Isaac Newtons second law of motion states that the time rate of change of momentum is equal to the force acting on the particle. Conservation of momentum of a particle is a property exhibited by any particle where the total amount of momentum never changes.
The force that keeps an object moving. The term momentum is commonly used in. Also momentum is clearly a vector since it involves the velocity vector.
To truly understand the equation it is important to understand its meaning in words. Whenever there is an interaction between two objects there is a force upon each of the objects. From Newtons second law it follows that if a constant force acts on a particle for a.
K ½mv 2. Spin is an intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles and thus by composite particles and atomic nuclei. The quality that keeps an event developing or making.
Linear momentum of a particle is a vector quantity and is denoted by. From these its easy to see that kinetic energy is a scalar since it involves the square of the velocity dot product of the velocity vector with itself. Angular momentum is a form of inertia reflecting the objects size shape mass and rotational velocity.
A dot product is always a scalar. In Newtonian mechanics linear momentum translational momentum or simply momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. Spin is one of two types of angular momentum in quantum mechanics the other being orbital angular momentumThe orbital angular momentum operator is the quantum-mechanical counterpart to the classical angular momentum of orbital.
It is important to understand that Eq. Now we want to extend the idea of the energy conservation law in an important wayin a way that says something in detail about how energy is conserved. 73 is a vector equation.
The new law will say that if energy goes away from a region it is because it flows away through the. Since one is a vector and the other is a scalar this means that kinetic energy and momentum will both be useful but in quite.
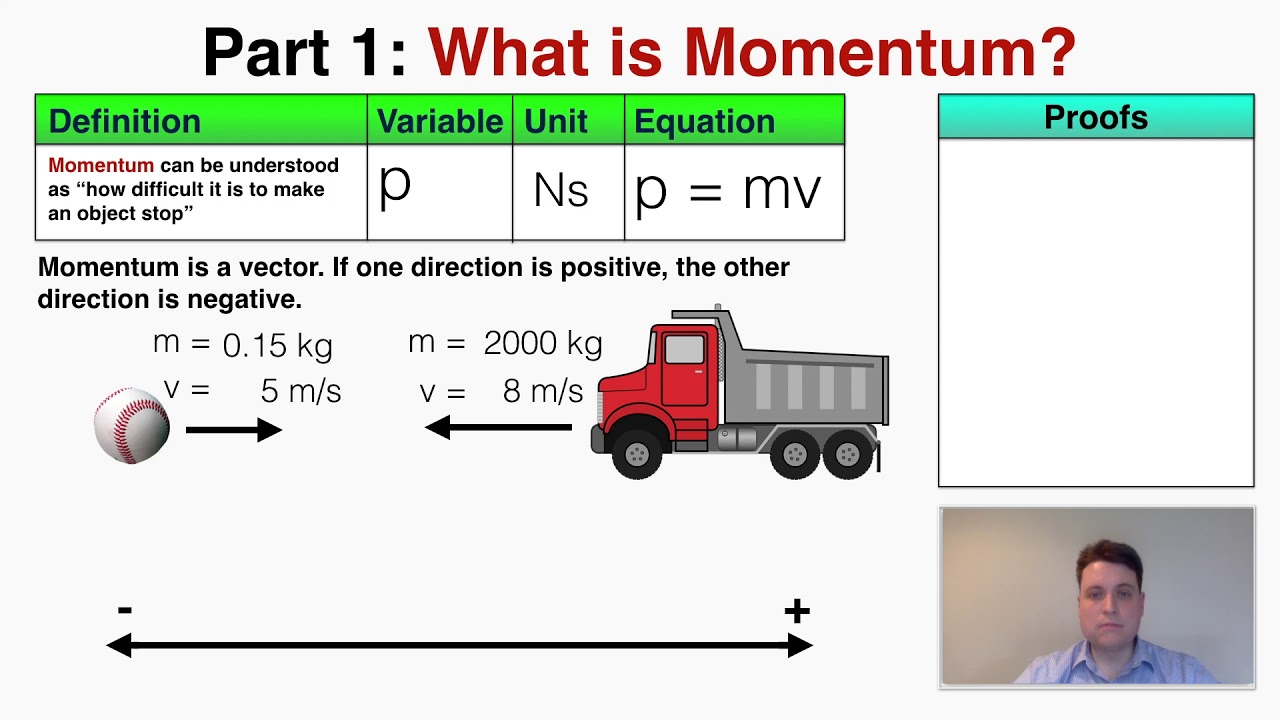
What Is Momentum Ib Physics Youtube
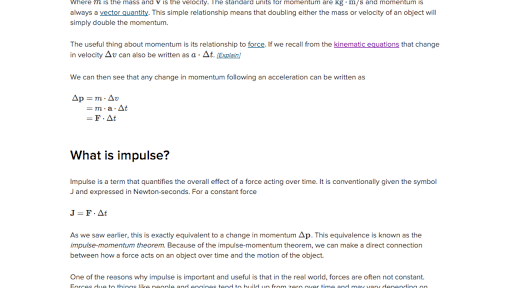
What Are Momentum And Impulse Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Momentum Meaning in Physics"
Post a Comment